AFM3D: An Asynchronous Federated Meta-learning Framework for Driver Distraction Detection
Published in IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024
Recommended citation: S Liu, L You, R Zhu, B Liu, R Liu, H Yu, and C Yuen, "AFM3D: An Asynchronous Federated Meta-learning Framework for Driver Distraction Detection", IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 25, no. 8, pp. 9659-9674, Aug 2024, doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3357138. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10423999
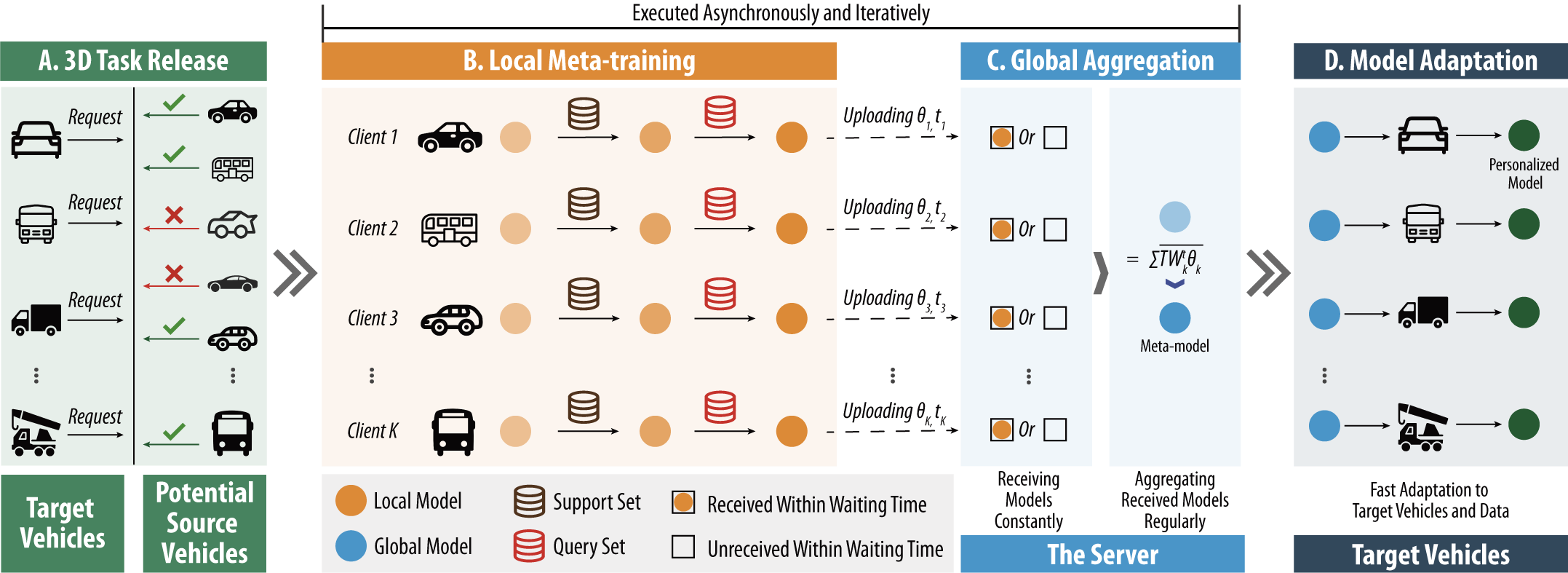
Abstract: Driver Distraction Detection (3D) is of great significance in helping intelligent vehicles decide whether to remind drivers or take over the driving task and avoid traffic accidents. However, the current centralized learning paradigm of 3D has become unpractical because of rising limitations on data sharing and increasing concerns about user privacy. In this context, 3D is further facing three emerging challenges, namely data islands, data heterogeneity, and the straggler issue. To jointly address these three issues and make the 3D model training and deployment more practical and efficient, this paper proposes an Asynchronous Federated Meta-learning framework called AFM3D. Specifically, AFM3D bridges data islands through Federated Learning (FL), a novel distributed learning paradigm that enables multiple clients (i.e., private vehicles with individual data of drivers) to learn a global model collaboratively without data exchange. Moreover, AFM3D further utilizes meta-learning to tackle data heterogeneity by training a meta-model that can adapt to new driver data quickly with satisfactory performance. Finally, AFM3D is designed to operate in an asynchronous mode to reduce delays caused by stragglers and achieve efficient learning. A temporally weighted aggregation strategy is also designed to handle stale models commonly encountered in the asynchronous mode and in turn, optimize the aggregation direction. Extensive experiment results show that AFM3D can boost performance in terms of model accuracy, recall, F1 score, test loss, and learning speed by 7.61%, 7.44%, 7.95%, 9.95%, and 50.91%, respectively, against five state-of-the-art methods.
Keywords: Driver Distraction Detection, Federated Learning, Asynchronous Federated Learning, Federated Meta-learning