FedRC: Representational Consistency Guided Model Uploading Mechanism for Asynchronous Federated Learning
Published in EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, 2023
Recommended citation: S Liu, L You, and Y Zhou, "FedRC: Representational Consistency Guided Model Uploading Mechanism for Asynchronous Federated Learning", EAI International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Computing, Networking and Services, 239-256, Jul 2024, doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63989-0_12. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-63989-0_12
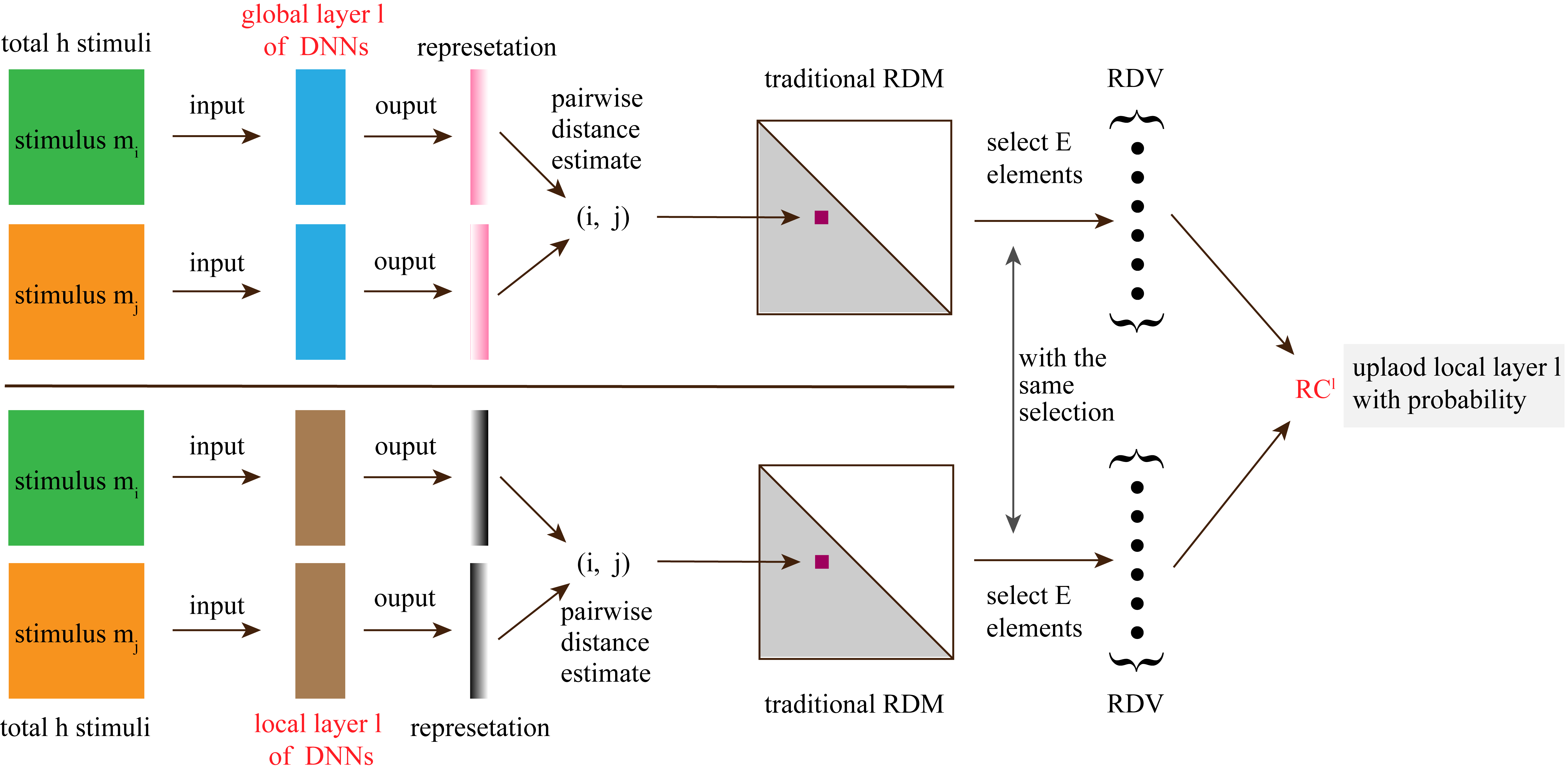
Abstract: Recently, a novel distributed machine learning paradigm called Federated learning (FL) has caught the eyes of both academics and industries, as it can orchestrate substantial Internet of Things (IoT) devices as clients to learn a global model collaboratively and efficiently without sharing sensitive data. Moreover, while comparing the two modes of FL, i.e., synchronous FL (SFL) and asynchronous FL (AFL), AFL is more scalable and flexible to address the issue of over-fitting and the performance bottleneck caused by the stragglers. However, the data heterogeneity and high communication consumption issues faced by AFL still hamper its further applications and deployments in ubiquitous IoT. Motivated by this, we propose FedRC, a model uploading mechanism for AFL, guided by Representational Consistency (RC). As a layer-wise uploading method for Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), FedRC calculates simplified Representational Dissimilarity Vectors (RDVs) for each local layer and corresponding global layer, respectively, after the local training of each client, and then measures RCs based on the two RDVs to adaptively determine the uploading of model layers. According to the evaluation based on three standard datasets, compared with four state-of-the-art baselines (i.e., FedAvg, FedProx, FedAsync, and PartialNet), FedRC can boost model accuracy by 3.48%, save communication costs by 26.79%, and shorten transmission time by 44.14%, respectively.
Keywords: Federated Learning, Asynchronous Federated Learning, Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), Model Uploading